How Computer Vision Technology is Improving Everyday Life
Computer vision is changing how we live and work. By allowing machines to interpret and analyze visual data, this technology is transforming industries and making everyday life more efficient. From healthcare and retail to automotive safety and security, computer vision is already embedded in systems we use every day, providing solutions that improve accuracy, speed, and convenience.
As more industries adopt these innovations, the benefits of computer vision are becoming increasingly clear. This article will explore how this technology is making life better, offering real-world examples of its applications across various sectors.
What is Computer Vision Technology?

Computer vision technology lets machines interpret and understand the visual world using AI algorithms and machine learning. It essentially gives machines “eyes,” enabling them to process images, videos, and real-time camera or sensor data.
By simulating human vision, computer vision applications identify objects, analyze facial expressions, or detect anomalies. The technology relies on deep learning, where neural networks are trained on large datasets to recognize patterns.
Though often linked with industries like self-driving cars, computer vision is already part of everyday life. It’s in smartphone facial recognition software, image search engines, and medical scanners that detect diseases earlier.
As technology grows, it will continue to change how we live and work, making tasks more efficient. Computer vision has vast applications in healthcare, retail, automotive, security, and education, improving daily life.
We are just beginning to explore its full potential.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
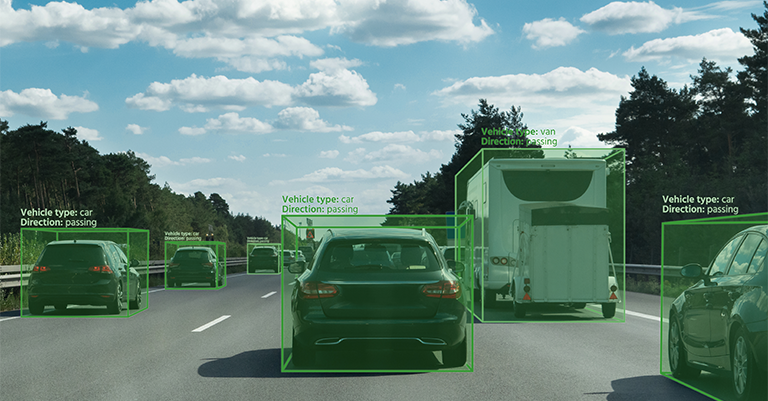
At its core, computer vision technology enables machines to interpret and understand visual data from the world around them. It mimics human vision but relies on complex algorithms and machine learning models to process images, videos, or real-time data streams from cameras and sensors. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
Image Acquisition
The first step in computer vision involves acquiring an image or video feed. Cameras, sensors, or any device capable of capturing visual data can perform this task. After acquisition, the system converts the raw image into a digital form that the computer processes.
Preprocessing the Image
Before analyzing the image, the system typically processes it in a preprocessing stage. This step improves image quality and reduces noise or distortions that could affect the analysis. Common techniques adjust brightness and contrast, resize the image, and filter out irrelevant data.
Feature Extraction
Next, the system identifies key features within the image that are relevant to the task at hand. For example, in facial recognition, the algorithm will focus on extracting features like eyes, nose, and mouth positions. In medical imaging, it might look for patterns like the shape of cells or the presence of anomalies. Feature extraction transforms the visual data into a more manageable format for analysis.
Pattern Recognition with Machine Learning
Here, artificial intelligence and machine learning take over. The system analyzes the extracted features using pre-trained machine learning models fed vast datasets of similar images. These models recognize patterns and make predictions based on the visual data. For example, a model trained on thousands of medical scans might detect early signs of cancer in new images.
Decision Making
The system makes decisions based on the analysis as it recognizes patterns. These decisions can range from simple tasks like identifying an object in a picture to more complex actions like flagging suspicious behavior in a surveillance feed or providing a medical diagnosis.
Feedback and Learning
One of the powerful aspects of computer vision is its ability to improve over time. As the system processes more images and gathers feedback, it learns from its mistakes and becomes more accurate. This continuous learning loop is essential in applications like autonomous driving, where the system must adapt to ever-changing environments.
By integrating these steps, computer vision technology enables machines to perform tasks that were once thought to require human perception. From recognizing faces and objects to interpreting complex medical images, the technology is redefining how computers “see” the world and apply that knowledge to solve real-world problems.
Real-Life Applications of Computer Vision Technology
Computer vision technology increasingly integrates into daily life, transforming industries and improving how we interact with the world. Its ability to interpret and analyze visual data drives many real-life applications. These applications make processes more efficient, safer, and smarter.
Below are some of the most common and impactful uses of computer vision technology in real-world scenarios.
Applications of Computer Vision in Healthcare
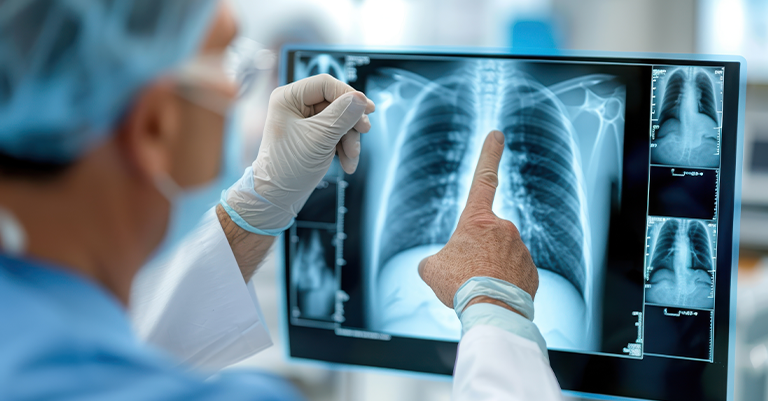
Healthcare has been one of the industries most positively impacted by computer vision technology. This technology can help doctors and medical professionals diagnose diseases faster and more accurately. One prime example is the use of AI to analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. In many cases, machine learning algorithms trained on large sets of medical data can detect issues like tumors or lesions with greater precision than human specialists.
Moreover, computer vision helps improve surgery. Robotic-assisted surgeries use computer vision to enhance the surgeon’s view, allowing for more precise cuts and less invasive procedures. These technologies can reduce recovery times for patients and lower the risk of complications.
Another promising area is patient monitoring. Cameras equipped with computer vision technology can track patient movements and behaviors in real-time, alerting caregivers to potential falls or other risks in elderly or high-risk individuals. This makes monitoring more proactive and reduces the burden on healthcare professionals.
By improving diagnostics, enhancing surgical outcomes, and providing better patient monitoring, computer vision technology is revolutionizing healthcare. It’s not only making medical treatments more effective but also more accessible, benefiting both patients and practitioners alike.
The Role of Computer Vision in Retail and E-commerce
In the retail and e-commerce industries, computer vision is transforming the way companies interact with customers and manage operations. One of the key benefits is enhancing the shopping experience through personalized recommendations and visual search features. Many online retailers now use image-based search engines that allow users to upload photos of products they want to find or replicate. The AI behind the system matches similar items in the store’s inventory, making it easier for customers to find exactly what they need.
Beyond customer experience, computer vision also plays a vital role in inventory management. Automated systems powered by AI can monitor shelves and update inventory in real-time. This reduces human error, ensures that stock levels are maintained, and even prevents theft or fraud in physical stores.
In warehouses, robots equipped with computer vision can sort and package products with minimal human intervention. This speeds up order fulfillment and allows for greater accuracy in delivery. As retail shifts more toward online shopping, the integration of computer vision technology will continue to streamline the supply chain, making businesses more efficient while offering customers a seamless experience.
Enhancing Automotive Safety with Computer Vision
Computer vision is at the heart of the growing field of autonomous vehicles. It enables cars to interpret and respond to their environment, reducing the chances of human error that lead to accidents. Through advanced cameras and sensors, vehicles equipped with this technology can identify pedestrians, cyclists, road signs, and other vehicles, allowing them to adjust speed, brake automatically, or even steer around obstacles.
One of the key features of computer vision in automotive safety is driver-assistance systems. These include lane departure warnings, automatic braking, and adaptive cruise control, all of which are designed to improve the safety of everyday driving. Even for drivers of traditional vehicles, these technologies can prevent accidents and save lives.
In addition to self-driving cars, computer vision also plays a significant role in traffic management and public transportation. AI-powered cameras can analyze traffic flow, identify congested areas, and optimize routes for buses and emergency vehicles. This results in smoother traffic, fewer accidents, and better fuel efficiency.
By making driving safer and more efficient, computer vision is not only transforming the automotive industry but also reshaping how we approach transportation in general.
Improving Security and Surveillance with Computer Vision
Security and surveillance have greatly benefited from advances in computer vision technology. AI-driven cameras can automatically detect suspicious activity, recognize faces, and even identify license plates in real-time. This has enormous potential for crime prevention and law enforcement.
In public spaces, computer vision can be used to monitor crowds and identify potential threats. For instance, it can detect unusual behaviors such as unattended bags or loitering in restricted areas, prompting faster responses from security personnel. This level of automation helps reduce human oversight, making it easier to maintain safety in large areas like airports, stadiums, and shopping centers.
In the private sector, companies are using computer vision to monitor workplace safety. Cameras can detect when employees enter hazardous zones or fail to wear proper protective gear, reducing workplace accidents. It also has applications in access control, where facial recognition technology replaces traditional keycards for building entry, ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter secure areas.
By combining real-time analysis with machine learning, computer vision is helping to make both public and private spaces safer and more secure.
Revolutionizing Education with Computer Vision
Computer vision has the potential to revolutionize the educational system in both classrooms and online learning environments. One of the most impactful applications is in remote learning, where computer vision can analyze student engagement by tracking facial expressions or eye movements. This allows teachers to better understand when students are confused or disengaged, even in a virtual setting.
In physical classrooms, computer vision can automate administrative tasks like attendance tracking by recognizing students as they enter and exit the room. This reduces distractions for teachers, allowing them to focus more on the lesson itself.
Additionally, augmented reality (AR) powered by computer vision can bring lessons to life in new ways. Imagine a history class where students can interact with 3D models of ancient artifacts or a biology lesson where they can examine human organs in AR. These experiences make learning more interactive and engaging for students of all ages.
By streamlining tasks and enhancing learning through AR and other tools, computer vision is helping teachers provide a more personalized and effective educational experience.
Challenges and Potential Problems
While computer vision technology has brought significant advancements across many industries, it also faces several challenges and potential problems that need to be addressed as the technology continues to evolve. These challenges range from technical limitations to ethical concerns, and understanding them is crucial to the responsible development and deployment of computer vision systems.
Data Privacy Concerns

One of the most pressing issues with computer vision is data privacy. The technology often involves collecting and analyzing vast amounts of visual data, such as images from surveillance cameras or facial recognition systems. This can raise concerns about how personal information is being used and stored. Unauthorized data collection, especially in public spaces, poses risks to individual privacy and opens the door for potential abuse or misuse of information.
Bias and Discrimination
Like many AI-driven technologies, computer vision systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on. If the training datasets are not diverse enough, the technology may struggle to accurately recognize individuals from different ethnicities, genders, or age groups. This bias can lead to discrimination, particularly in areas like facial recognition, where incorrect identifications could have serious legal or social consequences. For instance, biased algorithms could lead to wrongful surveillance or unequal treatment of certain groups.
Accuracy and Reliability
Despite the advances in computer vision, the technology is not always 100% accurate. Misidentifications or errors in visual data processing can have significant consequences, especially in critical applications such as healthcare, autonomous driving, and security. In self-driving cars, for example, even a small error in object recognition can result in accidents. Similarly, incorrect diagnoses in medical imaging can lead to improper treatment or missed diagnoses.
Computational Requirements
Computer vision systems often require immense computational power and large datasets to function effectively. This makes the technology resource-intensive and can limit its accessibility, particularly for smaller organizations or developing countries. High-end hardware, cloud storage, and powerful processors are essential for real-time image processing, and these requirements can be costly and create barriers to widespread adoption.
Security Vulnerabilities
Computer vision systems are also vulnerable to cyber-attacks, such as adversarial attacks where hackers manipulate visual inputs to deceive the system. For instance, in autonomous driving, attackers could alter road signs to trick the car’s computer vision system into making dangerous decisions. These vulnerabilities can undermine the reliability and security of AI-powered systems, leading to serious safety risks.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the continued growth and ethical use of computer vision technology. Solutions like better privacy regulations, unbiased data collection, improved algorithms, and enhanced cybersecurity measures will help mitigate these issues, ensuring that the benefits of computer vision can be realized without compromising safety or ethics.
The Future of Computer Vision and Everyday Life
As computer vision technology continues to evolve, its role in our everyday lives will only grow. In the coming years, we can expect more integration of this technology in areas like smart homes, healthcare, and even personal safety devices. For example, home security systems may become fully automated, capable of recognizing when a homeowner is present or when an unfamiliar person is at the door.
In healthcare, computer vision could expand beyond diagnostics to fully automated patient care systems that monitor and assist patients in real-time. As these technologies improve, the quality of care will increase while reducing costs and labor shortages in the medical field.
The possibilities are endless. Whether it’s improving the efficiency of our transportation systems, enhancing security, or enabling more immersive learning experiences, computer vision is poised to transform our daily lives in ways we’re only beginning to see.
Final Thoughts on Computer Vision
Computer vision technology is rapidly transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. From revolutionizing healthcare and enhancing retail experiences to improving automotive safety and boosting security, its applications are vast and impactful. By enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data, computer vision is solving real-world problems with greater accuracy and efficiency.
However, like any advanced technology, it comes with challenges. Issues like data privacy, bias, accuracy, and security need to be carefully addressed to ensure that the technology benefits everyone while minimizing risks. As developers and industries continue to refine computer vision systems, the potential for even greater positive change is enormous. In the coming years, we can expect computer vision to become more integrated into our everyday lives, providing smarter, safer, and more personalized experiences across multiple industries. By navigating these challenges responsibly, we can harness the full potential of computer vision to create a future that’s more efficient, innovative, and secure.





